A control valve is a device used in industrial systems to regulate the flow of fluids (liquids, gases, or steam) within a process.
Briefly, it contains a valve body and an actuator:
1. Valve Body: The main housing of the valve, which contains the fluid path and controls the flow.
2. Actuator: The mechanism that moves the valve stem or disk to open, close, or modulate the valve.
Actuators can be pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic.
Types of Control Valves:
Linear type
such as globe valves and gate valves:
Common for precise control; they use a linear motion to regulate flow.
Quarter turn type
such as ball valves and butterfly valves:
Use a rotary motion; effective for quick shut-off and moderate control.
Applications:
Process Industries: Oil and gas, petrochemicals, water treatment.
HVAC Systems: Regulating heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Power Plants: Controlling steam flow and cooling systems.
In essence, control valves are the workhorses of process control, ensuring that industrial systems operate efficiently, safely, and effectively.

WHAT's IP code? What does IP certificate use for?
Many people know that IP testing is a guarantee of a product's protection, but few realize that this testing does not include the product's operation. IP (Ingress Protection) testing is typically conducted in a non-operating state, primarily to isolate the evaluation of the enclosure's protective capabilities from the product's internal functions. Conducting IP rating tests on non-operating products provides a controlled environment to specifically assess the physical barrier that the enclosure offers against foreign objects and liquids, ensuring a consistent and reliable measurement of its protective effectiveness.
Therefore, when you need an absolutely waterproof product for electrical operation in water, please be sure to confirm that using the product in or underwater is not a problem. This is because IP testing only represents the tested water ingress protection of the enclosure and does not represent waterproof protection for using the product in water.

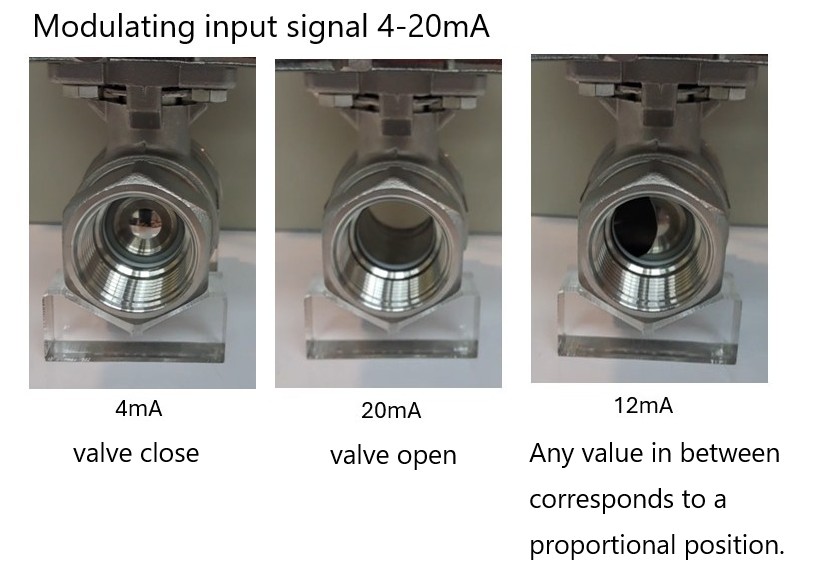
What does 4-20mA use for a quarter turn electric actuator?
The 4-20mA signal is commonly used for control and feedback in electric actuators and other industrial automation systems. Generally, the function named "modulating" with electric actuators. Here's how it works in an electric actuator:
1. Control Signal (Input to Actuator)
The 4-20mA signal is often used as an input command to control the actuator’s position, speed, or force.
4mA typically represents 0% (fully closed)
20mA represents 100% (fully open)
Any value in between corresponds to a proportional position.
2. Feedback Signal (Output from Actuator)
The actuator may also send a 4-20mA signal as a feedback to indicate its actual position.
This allows a control system (like a PLC or DCS) to monitor the actuator’s current status and make adjustments if needed.
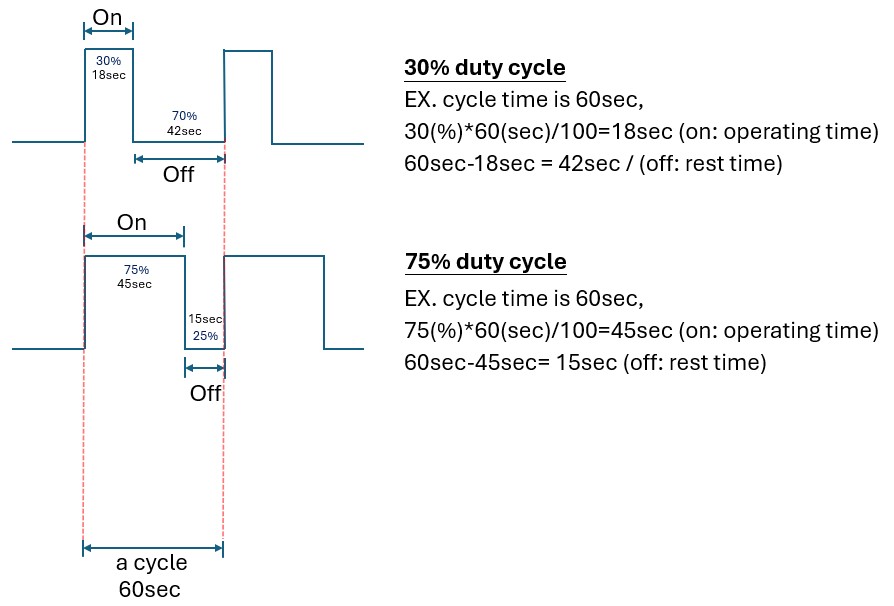
What's the duty cycle of electric actuators?
The duty cycle of an electric actuator refers to the percentage of time the actuator is in operation (moving or holding position) compared to the total time, including rest periods. This is particularly important in applications where the actuator needs to operate continuously or intermittently under load, as excessive operation without adequate rest can cause overheating or wear.
How Duty Cycle Works for Electric Actuators:
High-duty cycle actuators are designed to operate for long periods with minimal rest and are typically used in continuous or high-frequency applications.
Low-duty cycle actuators are intended for applications where the actuator only needs to operate occasionally, allowing it to rest most of the time.
For an electric actuator, a duty cycle might look like this:
Example: 30% duty cycle – The actuator can run for 30% of a given period and must rest for the remaining 70%. If the cycle time is 60 secs, this means the actuator can run for 18 secs and must rest for 42 secs.
Key Factors Affecting Duty Cycle of Electric Actuators:
Load and Force Requirements: Higher loads often require more frequent rest periods, reducing the duty cycle.
Motor Type: Actuators with different motor types (e.g., AC, DC, stepper, or servo motors) have varying duty cycle capabilities.
Heat Dissipation: The ability of the actuator's motor to dissipate heat
during operation directly impacts the duty cycle.
Environmental Conditions: Operating in extreme temperatures or harsh environments can affect the actuator's performance and duty cycle.
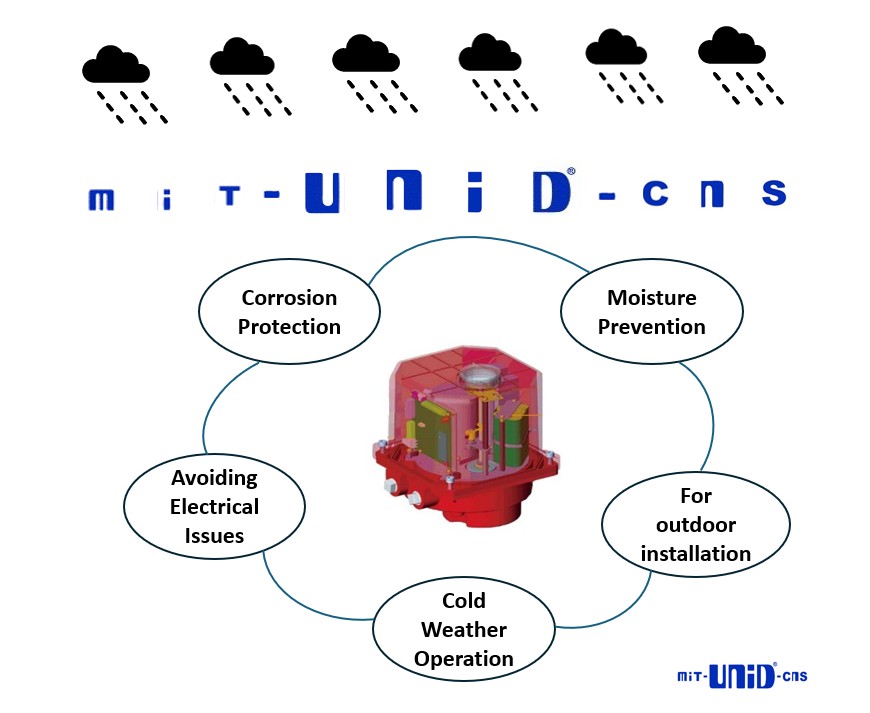
Ever wondered why your electric actuator might come with a built-in heater?
The purpose of a heater in an electric actuator is primarily to prevent the buildup of moisture and condensation inside the actuator's housing. Here's why this is important:
1. Moisture Prevention:
In environments with fluctuating temperatures, condensation can form inside the actuator. Moisture can damage internal electrical components, such as circuits, motors, and sensors.
2. Corrosion Protection: Condensation can lead to corrosion of metal parts, reducing the lifespan and reliability of the actuator.
3. Avoiding Electrical Issues: Moisture inside the actuator can cause short circuits or insulation breakdown, leading to malfunctions or safety hazards.
4. Cold Weather Operation: In cold climates, heaters can prevent the formation of ice inside the actuator, ensuring smooth operation. A Crucial Component for Reliable Performance.
In conclusion, the heater is more than an accessory—it’s a critical component that ensures the longevity, safety, and reliability of electric actuators in challenging environments. Whether protecting against moisture, corrosion, or freezing conditions, this small but mighty device plays an essential role in maintaining uninterrupted operation.
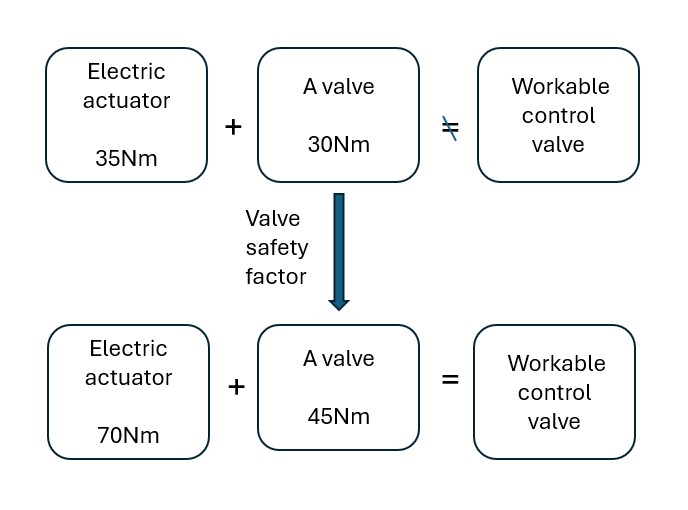
What could be a serious problem if you forget to include a valve safety factor
when select an electric actuator to connect?
The answer is that the electric actuator might fail to operate the valve.
For example, if you select an electric actuator with 35 Nm torque and a ball valve requiring 30 Nm torque, you might think they can function together without issues. However, valves always require a safety factor to compensate for additional torque caused by factors such as fluid impurities, working pressure, or fluid temperature. Generally, when matching electric actuators to valves, a safety factor of 1.3 to 1.5 times the valve torque should be added. For valves with larger torque requirements, a higher safety factor is necessary.
How many types do we have of electric actuators?
PRO UNI-D CO., LTD created three types of quarter turn valves (to control ball valves, butterfly valves, dampers...)
and one type of linear valves (gate valves, globe valves...). Both of them are able to add functions, such as
bluetooth control, failsafe, power backup, heater, supply Mobus ASCII through RS-485.
What's the connecting way of Modbus ASCII with RS485 of electric actuator?
Our smart type of electric actuators support Modbus ASCII that use RS485 to connect 2pcs~30pcs electric actuators in the same time. The program can control all electric actuators or some of them in sync or out of sync.What's the difference between electric actuator and linear valve actuator?
1. Electric actuators use to connect to quarter valve, such as ball valve, butterfly valves.2. Linear valve actuators use to connect to linear valves, such as gate valve
and global valves.
What is Bluetooth / WiFi control of electric actuator?
Our smart type of electric actuators with built-in bluetooth / WiFi function.Users can remote control valve open or close, detect electric actuators.
operating status and find problems for maintenance.
What's the dry contact (extra limit switch) function?
This is a volt free feedback signal that to advice electric actuator the status of valve.(Valve is opened or closed.)
What does electric actuators use for?
Electric actuator is a control device that connect to valve and control valve open and close.How to select a correct electric actuator?
1. Both of electric actuator and valve are with torque.2. Make sure the valve size, valve torque, and connecting standard that you will use:
ex. 2" stainless steel ball valve, NPT thread end, 60Nm (Newton metre).
3. Add safety factor 1.5 times on valve torque
ex. valve torque is 60Nm (Newton meter) *1.5 = 90Nm,
the electric actuator torque must be higher than 90Nm.
